Governor’s Proposed State Budget for 2024-25
Research Brief
Governor’s initial proposal for 2024-25 budget addresses large deficit without significant cuts or increases to public education funding
On January 10, Governor Newsom presented his initial budget proposal for the upcoming fiscal year. With tax receipts down this year and the late tax deadline last year, the Department of Finance is estimating a $37.9 billion budget deficit in the year ahead. Despite the shortfall, Governor Newsom did not propose significant cuts to education, instead essentially funding K-14 education at a similar level to the current year.
Legislative Update: Newsom’s Proposed State Budget ‘24-25
Initial Overview
January 11, 2024
Governor Newsom presented his initial 2024-25 budget proposal yesterday, with less dire projections than had been anticipated. The $291 billion budget proposal is about 6% smaller than the total 2023-24 budget, and about 8% smaller than the General Fund spending approved in the 2023-24 budget act.
The budget deficit as calculated by the Department of Finance (DOF) is estimated at $37.9 billion for the coming fiscal year; this is about $30 billion lower than the Legislative Analyst projected last month.
State budget for 2023-24
Protects public education with ongoing funding; staffing crisis requires more support
State budget for 2023-24 protects public education with ongoing funding; staffing crisis requires more support:
Governor Newsom and the state Legislature came to an agreement in late June on a budget for 2023-24 that includes $225 billion in general fund expenditures while addressing a $31.7 billion deficit.
The Proposition 98 funding minimum guarantee is $108.3 billion in 2023-24, which is less than what last year’s enacted budget assumed, but slightly higher than the revised guarantee for 2022-23.
Governor’s Proposed State Budget for 2023-24
Research Brief
Governor Newsom started off the 2023-24 budget process on January 10 with a $223.6 billion proposal. Facing lower revenues than expected last year and a budget deficit projected at $22.5 billion by the Department of Finance, the January budget proposal is cautionary. Since the 2022-23 enacted budget anticipated a different budgetary landscape and included significant one-time expenditures, the governor’s initial proposal includes few cuts to education and does not draw on the available rainy-day reserves. Protecting education funding, the proposal also fully funds the statutory COLA, which is estimated at 8.13% at this time.
CFT to sponsor essential legislation for 2023-2024 legislative session
Legislative Update
INTRODUCTION
With the 2023-2024 California Legislative Session beginning, the CFT will be engaging in a new environment at the state Capitol. With several education champions reaching their term limits, and a large sector of the legislative staff turning over, the Legislative Department will be focusing on building new relationships with newly-elected legislators and their staff.
Governor signs six CFT bills, plus budget trailer bills with union priorities
Legislative Update
Governor Newsom signed six union bills at the end of September that the CFT successfully lobbied in both houses of the Legislature. The CFT had sponsored or co-sponsored 16 legislative bills alongside several budget proposals in the last year of the 2020-22 legislative session. A majority of these priorities made it to the governor’s desk or were included in the state budget, with only one bill being vetoed by the governor.
What budget trailer bills mean for education workers
Legislative Update
On September 30, Governor Newsom signed the final budget trailer bills sent to him by the Legislature after passing the bills and a “budget junior” on August 31. Budget trailer bills are created by the Committee on Budget to provide technical language for the implementation of fiscal allocations. The budget junior bill includes additional allocations as well as additional items necessary for implementation of some July budget expenditures.
The budget-related bills go into effect immediately. CFT priorities in the budget trailer bills are listed below.
State budget continues record funding for public education, secures funding for part-time faculty healthcare
Legislative Update
Funding for part-time community college faculty healthcare secured
Governor Newsom signed the final state budget on Friday, June 30 after the governor and state legislators reached agreement on the 2022-23 budget over the weekend. The deal includes record levels of funding for public education and the $200 million to support part-time faculty healthcare that CFT has been championing throughout this budget process.
CFT analyzes governor’s proposed budget for 2022-23
Research Brief
Governor Newsom introduced a $286.4 billion budget proposal for 2022-23 on January 10. The proposed budget is 9% larger than last year’s record high budget, largely because of tax receipts that were even higher than expected. The governor’s office is anticipating a $21 billion discretionary surplus for 2022-23 and this includes billions more for education.
Education sees another increase in governor’s state budget proposal
Legislative Update
Governor Newsom proposed significant increases for education and a 5.33% Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) in his state budget for 2022-23 released January 8. In his proposal, the governor addressed five concurrent state crises — COVID-19, climate change, inequality, homelessness, and public safety — several of which are reflected in the education budget. This budget is a preliminary proposal subject to negotiations with the Legislature and will be revised in May, with its final passage in June.
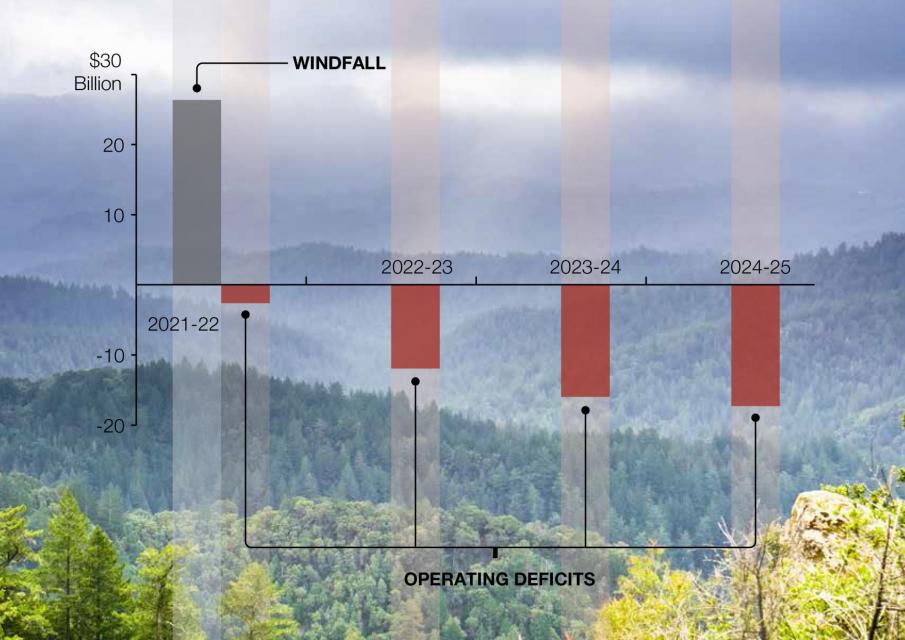
LAO predicts $31 billion budget surplus for 2022-23
Research Brief
Each November, the Legislative Analyst’s Office (the non-partisan advisor for the state Legislature) prepares a fiscal outlook in anticipation of the state budget process that kicks off in January with the governor’s budget proposal.
Overall, revenues are growing at historic rates and the LAO estimates the state will have a $31 billion surplus to allocate in 2022‑23. The Proposition 98 guarantee for schools and community colleges is estimated to be $11.6 billion (12.4% above the 2021-22 enacted budget). LAO estimates $9.5 billion will be available for new commitments and $10.2 billion will be available for one-time spending.
State budget adopted for 2021-22 boasts all-time high for education spending
Research Brief
Governor Newsom and the state Legislature came to an agreement on a $263 billion budget that reflects the state’s extraordinary surplus and billions from the latest round of federal stimulus funding from the American Rescue Plan. Spending for K-12 education totals $123.9 billion and is at an all-time high, including the largest ever allocation of Proposition 98 funding for schools and community colleges.
What’s in the largest ever state education budget?
Legislative Update — historic investment coming in 2021-22
On July 9, Governor Newsom signed a historic education budget with an unprecedented investment in our students and schools.
The California Legislature voted on and passed identical budget bills (AB/SB 129) on June 28, after reaching agreement with the governor about most budget issues. The full budget is $263 billion, thanks to an extraordinary surplus and the latest round of federal stimulus funding from the American Rescue Plan. A few outstanding details will be finalized in trailer bills.
Governor’s May Revision proposes highest level of education funding in California history
Legislative Update
California began the previous budget year with a looming recession forecasted due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and a projected $54 billion deficit. However, due mostly to the inequitable recovery of the stock market, profits from Silicon Valley, and high-income earners that did not lose their jobs, the state now has projected a $75.7 billion surplus.
CFT analyzes governor’s proposed education budget for 2021-22
Research Brief
Governor Newsom introduced his proposed $227 billion budget for 2021-22 on January 8. The proposed budget is starkly different from what lawmakers anticipated when they finalized the 2020-21 budget, largely because of much larger than expected tax receipts.
Governor’s budget proposes increases for education, financial incentive to return to in-person
Legislative Update
Gov. Newsom released the annual January budget proposal for the 2021-22 budget year, totaling $227.2 billion on Friday, January 8. The budget is very different from what lawmakers anticipated six months ago, when the 2020-21 budget was finalized, thanks to much larger than expected tax receipts. The proposal includes $34 billion allocated to reserves (including the Public School System Stabilization reserve) and as discretionary surplus funding.
Governor proposes record education funding in state budget
To cap a tumultuous week, today Governor Newsom announced his state budget proposal for the coming year. Despite a struggling economy, and high unemployment, the top line budget numbers are hopeful for public education: a record $85.8 billion for K-14 schools, along with additional funding for teacher recruitment and training, and special education, among other programs. Additionally, the governor estimates that there will be an additional $6.7 billion from the federal government for K-12 as part of the most recent stimulus package.
Legislative Analyst forecasts state revenue windfall for 2021-22
Legislative Update
Each November, the Legislative Analyst’s Office (LAO) is tasked with providing the state Legislature with forecasting of the state’s revenue and budget constraints. Those numbers have just been released to provide a starting point for what to expect in budget negotiations for the California 2021-22 state budget.
Education budget trailer bill addresses COVID-related issues
Research Brief
Governor Newsom signed Senate Bill 820 into law on September 18, 2020. This budget trailer bill is a technical clean-up bill for Senate Bill 98, which was signed into law on June 29 as part of the 2020-21 state budget. SB 820 contains several clarifications that have an impact on early childhood, preK-12 schools, and higher education.
Major provisions of this bill affect both schools and community colleges. They are listed first, followed by more provisions specific to each division. You can also download our pdf version.
MAJOR PROVISIONS
Revises deadlines for spending COVID-19 learning loss mitigation funds
- $355.2 million of these funds are from the Federal Trust Fund. The deadline for spending these funds is extended by one year, to September 30, 2022 (previously Sept. 30, 2021).
- $539.9 million of these funds are from the state General Fund. The deadline for spending these funds is extended to June 30, 2021 (previously Dec. 30, 2020).
- $4.4 billion of these funds are from the Coronavirus Relief Fund and there is no change to the deadline for spending these funds (December 30, 2020).
Broadens eligibility to more districts for low-cost borrowing
- Allows school and community college districts, and county offices of education, to use the California School Finance Authority (CSFA) intercept, which will enable those districts to lower borrowing costs to address state funding deferrals.
Broadens use of funding for instructional materials and lottery funds
- Existing law defines “instructional materials” and “technology-based materials” such that it excludes electronic equipment and could prohibit a school district from purchasing computers or related equipment. The bill deletes language that excludes electronic equipment from the definition of technology-based materials and the provisions prohibiting the replacement of computers or establishing a new computer lab. It specifies that technology-based materials also include the electronic equipment required to make use of those materials used by pupils and teachers as a learning resource, including, but not limited to, laptop computers and devices that provide internet access.
- Clarifies the definition of “instructional materials” in a new section of the Government Code, which will allow schools and community colleges to use lottery funds to purchase instructional materials. It specifies that instructional materials “include, but are not limited to, laptop computers and devices that provide internet access for use by pupils, students, teachers, and faculty as learning resources,” and provides more flexibility in the use of these funds.
PreK-12 SCHOOLS
Provides funding for enrollment growth
- Amends the Budget Act to allow Local Educational Agencies (LEAs), for their 2020-21 apportionment, to apply for either planned increases or actual planned growth to classroom-based student attendance in lieu of the 2019-20 average daily attendance (ADA) hold-harmless guarantee adopted in the Budget Act of 2020-21 under certain conditions.
- Excludes non-classroom-based charter schools from eligibility for enrollment growth funding.
Provides additional support for early childhood education/child care providers
- Clarifies that funding for child care providers located on an LEA campus qualifies for the hold harmless provision in the Budget Act, if the LEA is closed per public health guidance or order.
- Increases funding by $31.25 million in federal Child Care and Development Block Grant funds (CCDBG) and increases allowable non-operative days for alternative payment program providers by another 14 days (for COVID-19 related closures).
- Extends the waiver of family fees for child care services through Aug 31, 2020, and waives family fees for the 2020-21 fiscal year.
Updates other deadlines and requirements
- Executive Order N-66-20 authorized postponement of various educator assessment requirements, including attaining all other credential requirements, during the pandemic. The trailer bill extends the postponement to August 2021.
- Physical Performance Test for 2020-21 is suspended.
- The Budget Act postponed the deadline for developing an observation protocol for teaching English Language Learners to 2021. This trailer bill postpones it an additional year to 2022.
- The timeline for initial assessment of pupils for English language proficiency using the English Language Proficiency Assessment for California (ELPAC) is extended by 45 calendar days for the 2020-21 fiscal year. LEAs are required to screen new pupils, pending assessment results, to ensure those informally determined to be English learners receive appropriate supports as soon as possible.
Increases funding for summer meal program
- Increases the 2020-21 Budget Act appropriation for the COVID closure and summer meal program state reimbursement from $112 million in CARES Act funds to a total of $192 million through a combination of federal and general funds to reimburse LEAs.
Clarifies use of online instruction
- Clarifies that LEAs are not prohibited from adopting online instruction as part of a distance learning program and clarifies that except as required under a distance learning program, individuals may not record an online course without teacher and principal consent.
Extends encumbrance date of Community Schools Partnership Grant funds
- Amends the date by which grant funds from the California Community Schools Partnership Program must be encumbered to September 22, 2022, to align with the availability period for the federal Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) funds.
Amends appropriation for California Dyslexia Initiative
- Amends the appropriation for the Dyslexia Initiative to reflect $2 million in one-time Proposition 98 General Fund and $2 million in one-time federal funds instead of $4 million in one-time federal funds.
COMMUNITY COLLEGES
Expands Community College Board of Governors
- Adds the Lieutenant Governor as a voting member to the Board of Governors
UNIVERSITY
Allows University of California to use savings to avoid layoffs
- As of Jan. 1, 2021, General Fund capital expenditures may proceed only after certification that cleaning, maintenance, groundskeeping, food service, and other work traditionally performed by UC employees may not be outsourced.
- Authorizes UC to use savings from refunding, retiring, or restructuring bond debt to mitigate impacts to programs and services that predominantly support underrepresented students and to provide for continued employment for employees without layoffs, furloughs, and reductions in time.
MORE INFO
For additional information about SB 820, please contact:
Aimee Shreck Research Director
Ron Rapp Legislative Representative
Telephone (916) 446-2788
CFT says “Tax Billionaires”
We can’t cut our way to the economic recovery our students deserve!
As we navigate the global COVID-19 pandemic, Californians are experiencing crises that reach far beyond the immediate public and personal health emergencies. The poorest Californians, disproportionately people of color in the service, hospitality, and healthcare sectors, have either lost their jobs, resulting in a spike to unemployment unlike anything we have seen in our lifetimes, or are risking their health performing essential frontline services.
How to avoid catastrophic cuts to education and vital social services
OPINION: Tax the super rich
By Jim Miller, AFT Guild, Local 1931
The COVID-19 crisis and subsequent economic collapse along with the national uprising against police brutality and systemic racism have cast a glaring light on the nature of American inequality on the healthcare, criminal justice, and economic fronts. It has never been clearer that as most Americans struggle, the elite thrive.
Pandemic leads to big cuts for education in May Revision
Legislative Update
Governor Newsom released the May Revision to the 2020-21 state budget on May 14. California began 2020 with a solid fiscal foundation. As the proposal notes, the state started the year with a “strong and diverse economy, historic reserves, and a structurally balanced budget.
The state had eliminated past budgetary debts and deferrals and was making extraordinary payments to reduce pension liabilities. In January, a budget surplus of $5.6 billion was projected for the 2020-21 fiscal year. Revenues through March were running $1.35 billion above projections.
Uncertainty surrounds education budget for coming year
The one known — coronavirus has blown a giant hole in the state budget
The governor and the Legislature know the COVID-19 pandemic has blown a huge hole in the state budget, but they can’t easily project state revenues or the impact on Proposition 98 — the mechanism that provides K-12 schools and community colleges about 40 percent of the state’s General Fund.
Gov. Newsom prioritizes education in budget proposal
Legislative Update
Gov. Newsom released his $222 billion state budget proposal for 2020-21 on Friday, January 10. The proposal continues to invest in his education priorities, including early childhood education, special education, educator recruitment and training, as well as student health and wellness.
State Education Budget: Highlights and lowlights in governor’s initial proposal
On January 10, Gov. Brown released his proposed budget for the 2017-18 fiscal year amidst uncertainty about how federal actions may impact California. Federal funds currently account for more than one-third of the state budget, and according to the California Budget & Policy Center, 7.9 percent of federal dollars currently go to K-12 education and 5.2 percent to higher education.
State budget: Governor says voters need to renew Prop. 30 extension
How does the May Revision stack up for educators?
Gov. Brown made it clear in his May Revision that unless voters renew Proposition 30 in November, California will have to make budget cuts in future years.